A complete guide to building muscle, sustaining energy, and staying lean on a vegetarian diet—7-day high-protein plan, grocery list, timing strategy, and expert tips.
🌱 Introduction: Can You Get Enough Protein Without Meat?
Modern nutrition research is clear: a well-planned vegetarian diet can deliver all essential amino acids and support strength, muscle gain, and high energy levels. This guide shows how—plus a 7-day meal plan, grocery list, and practical, expert-based advice.
Before you start, estimate your needs with the Protein Calculator and Calories Calculator so you can tailor portions for muscle gain, fat loss, or maintenance.
🧬 Understanding Protein and Why It Matters
Protein supports enzymes, hormones, muscle repair, and healthy skin & hair. Nine amino acids are “essential,” meaning you must get them from food. Animal sources are typically complete; plant sources can be combined to form complete profiles.
🧩 The Challenge
Vegetarian diets sometimes fall short due to planning, not lack of options—insufficient variety and poor amino acid pairing are common pitfalls.
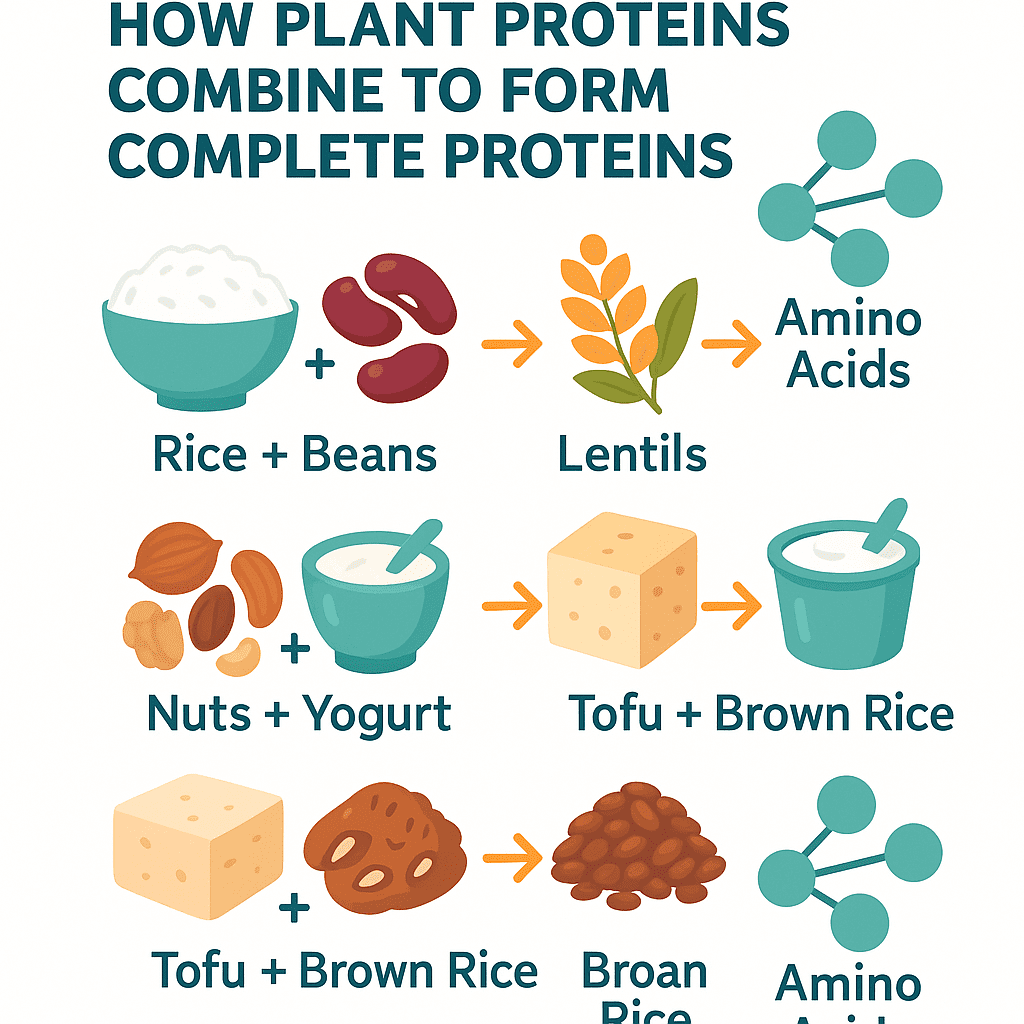
💡 The Solution: Smart Pairings
- Rice + beans
- Lentils + whole wheat
- Nuts + yogurt
- Tofu + brown rice
Together, these form complete proteins to cover amino acid gaps.
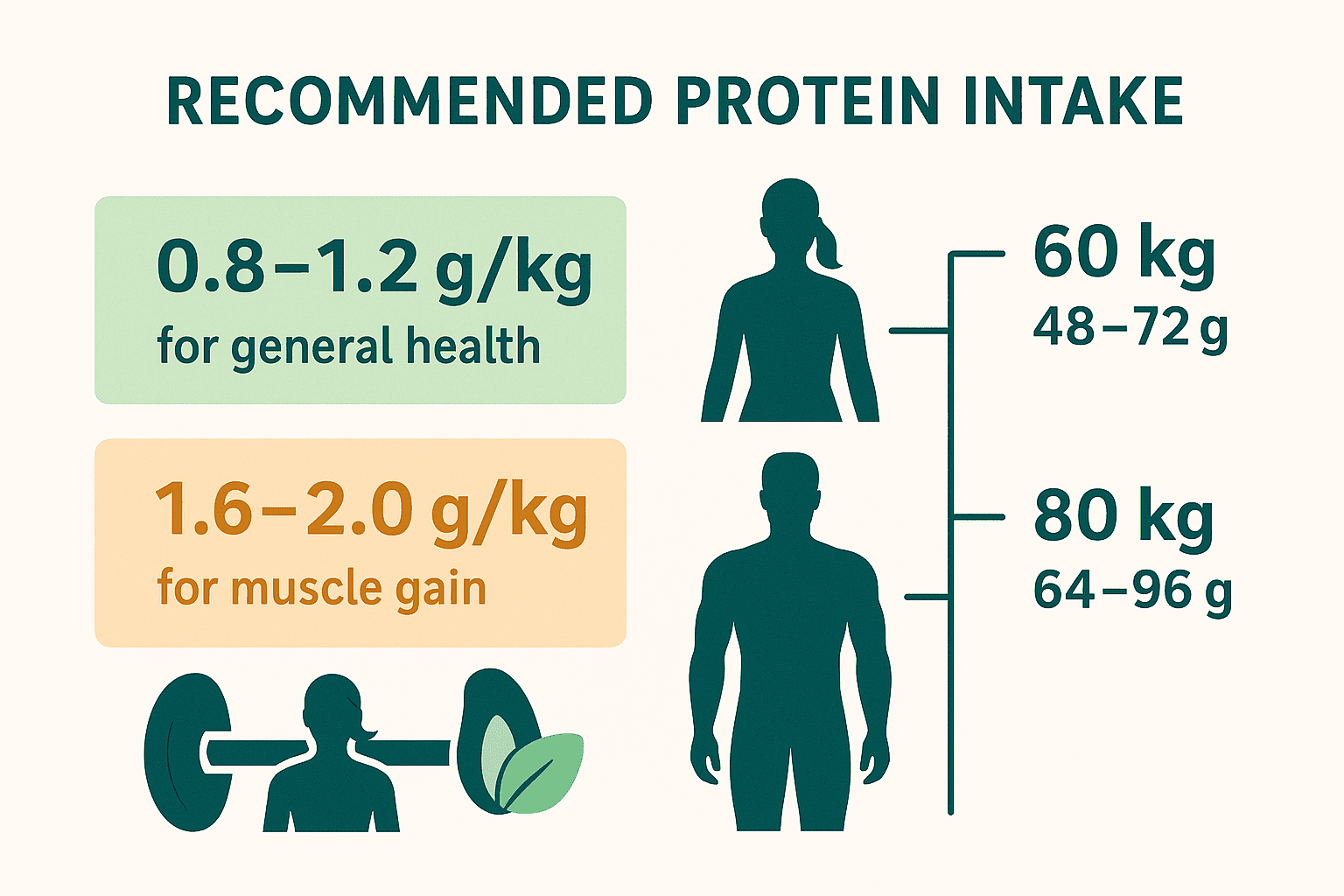
🥦 How Much Protein Do You Need per Day?
General health: ~0.8–1.2 g/kg body weight/day. For hard training or muscle gain: ~1.6–2.0 g/kg.
Example: 70 kg active person → ~110–130 g/day.
Get a personalized target with the Protein Calculator.
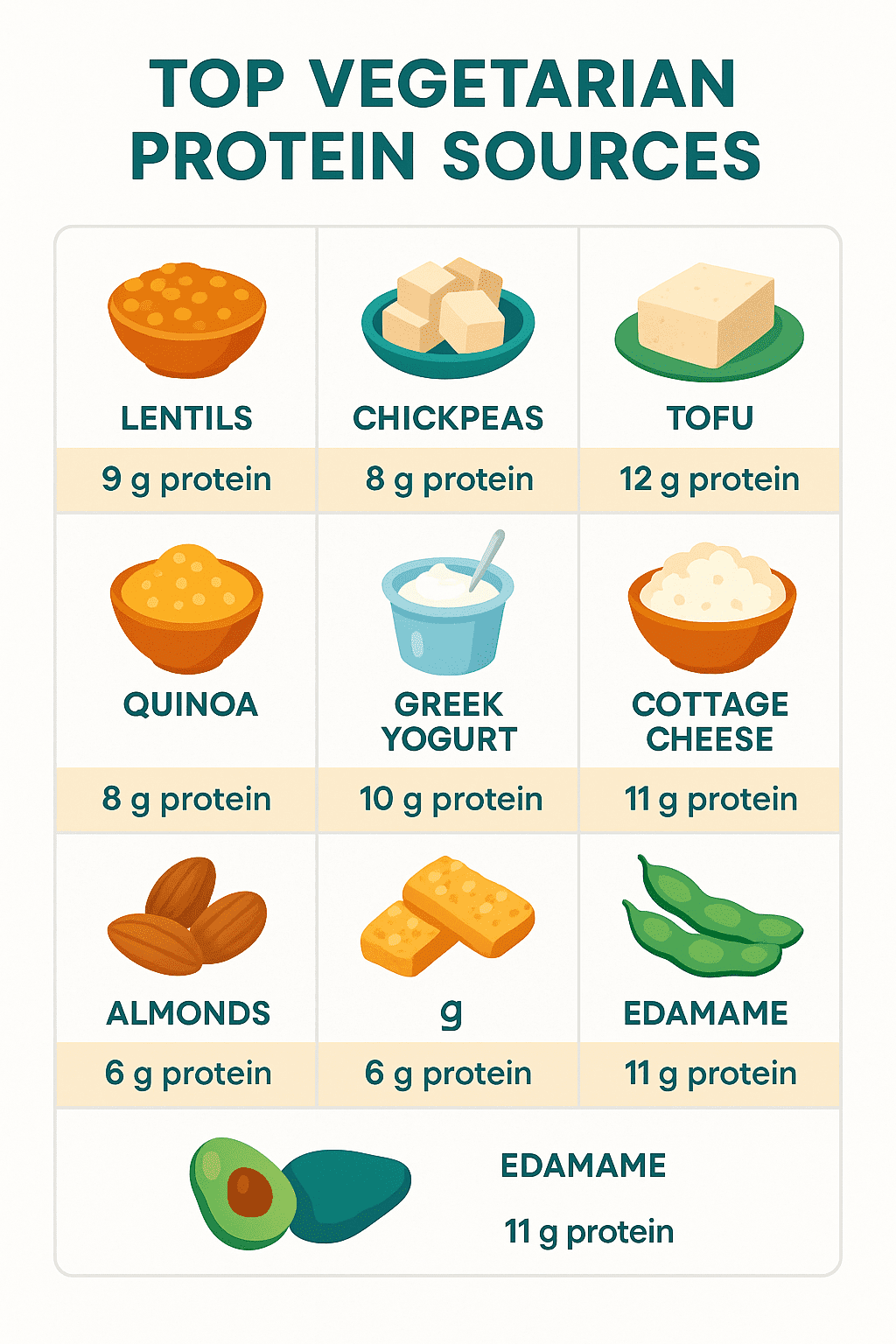
🥗 Top Vegetarian Protein Sources
| Food | Protein (per 100 g) | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Lentils | ≈9 g | High fiber & iron |
| Chickpeas | ≈8 g | Great for salads & curries |
| Greek yogurt | ≈10 g | Dairy complete protein |
| Tofu | ≈12 g | Versatile soy protein |
| Tempeh | ≈19 g | Fermented; digestible |
| Quinoa | ≈8 g | Complete plant protein |
| Cottage cheese | ≈11 g | Slow-digesting casein |
| Almonds | ≈6 g | Vitamin E & healthy fats |
| Eggs (ovo) | ≈13 g | Complete; highly bioavailable |
| Edamame | ≈11 g | Convenient snack |
Tip: Mix multiple plant proteins for better absorption and amino acid balance.
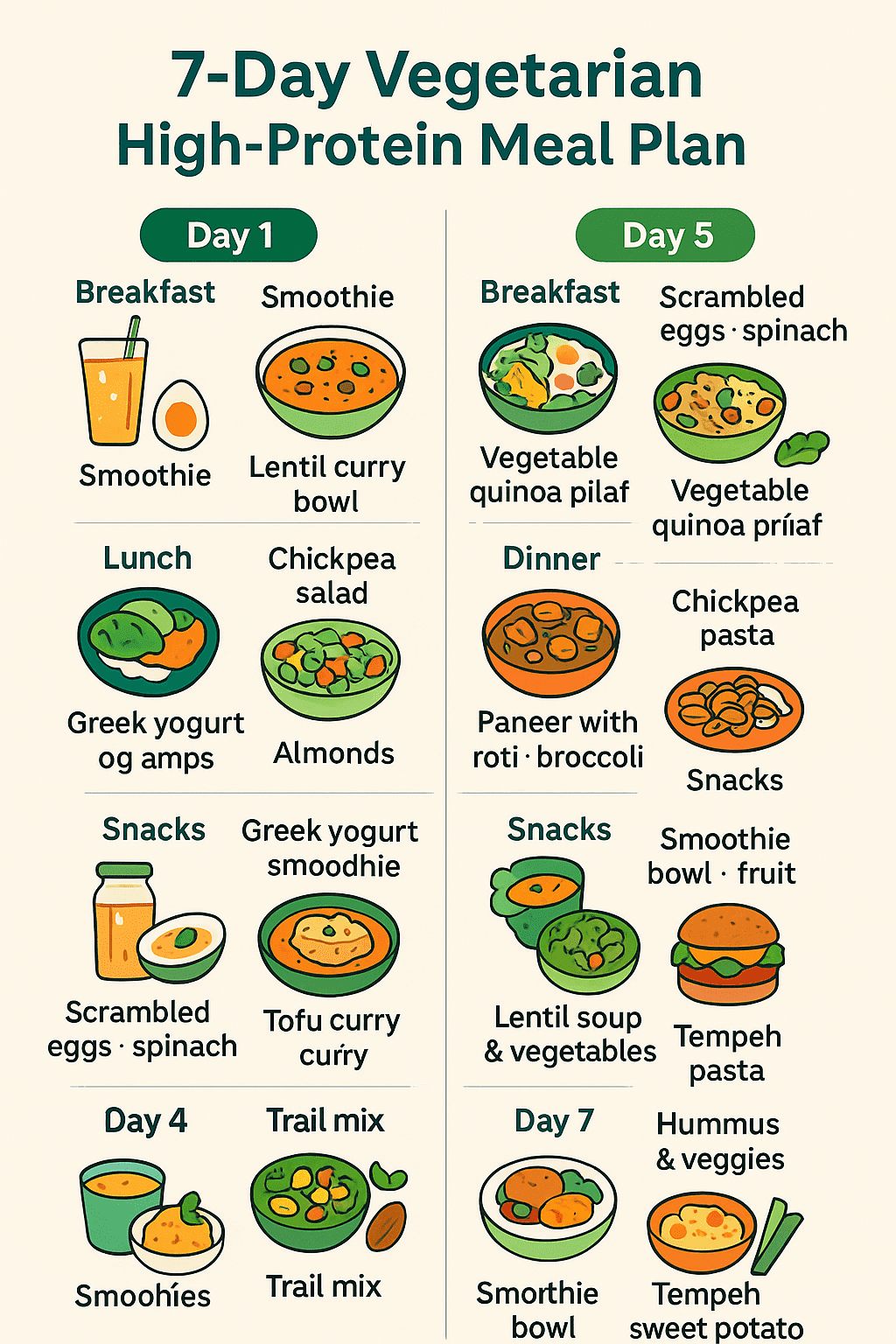
📅 7-Day Vegetarian High-Protein Meal Plan
~1,800–2,000 kcal and ~100–120 g protein daily. Adjust portions with the Calories Calculator.
🥣 Day 1: Power Start
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with chia, walnuts, blueberries
- Snack: Protein smoothie (soy milk, banana, protein powder)
- Lunch: Lentil curry, brown rice, side salad
- Snack: Roasted chickpeas
- Dinner: Tofu stir-fry with quinoa & mixed vegetables
💡 Make extra tofu for Day 2 lunch.
🍛 Day 2: Energizing Simplicity
- Breakfast: Veg omelet + whole-grain toast (or tofu scramble if vegan)
- Snack: Almonds + green tea
- Lunch: Chickpea salad with olive-oil dressing
- Snack: Cottage cheese + flaxseeds
- Dinner: Red lentil soup, brown rice, sautéed spinach
🌯 Day 3: Fiber & Protein Boost
- Breakfast: Oats with soy milk, chia, berries
- Snack: Boiled egg + apple
- Lunch: Quinoa bowl with kidney beans, avocado, tomato
- Snack: Hummus with cucumber & carrots
- Dinner: Paneer tikka, steamed broccoli, whole-wheat roti
🧆 Day 4: Balanced for Recovery
- Breakfast: Protein smoothie (peanut butter + banana)
- Snack: Trail mix (almonds, raisins, sunflower seeds)
- Lunch: Tofu curry, brown rice, cucumber raita
- Snack: Greek yogurt + honey
- Dinner: Lentil soup + mixed-veg stir-fry
🥗 Day 5: Light Yet Filling
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs (or tofu) + spinach
- Snack: Cottage cheese + pineapple
- Lunch: Vegetable quinoa pilaf with lentils
- Snack: Roasted edamame
- Dinner: Chickpea pasta with tomato sauce & olive oil
🍜 Day 6: Muscle Recovery Focus
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with peanut butter & banana
- Snack: Whey or soy protein shake
- Lunch: Tofu salad with avocado & kale
- Snack: Greek yogurt + chia seeds
- Dinner: Paneer curry with brown rice & peas
🍲 Day 7: Weekend Reset
- Breakfast: Smoothie bowl (oats, almond butter, flaxseeds)
- Snack: Walnuts
- Lunch: Lentil burger on whole-grain bun + salad
- Snack: Hummus + veggie sticks
- Dinner: Tempeh stir-fry with broccoli & sweet potatoes
🛒 Grocery List for a Protein-Rich Vegetarian Diet
🥦 Proteins
- Lentils, chickpeas, red/black/kidney beans
- Tofu, tempeh, paneer, Greek yogurt
- Eggs (optional)
- Cottage cheese
- Edamame, hummus
🌾 Carbohydrates
- Brown rice, quinoa, oats
- Whole-grain bread or roti
- Sweet potatoes
🥑 Healthy Fats
- Olive oil, coconut oil
- Almonds, walnuts, cashews
- Chia, flax, pumpkin seeds
🥕 Vegetables & Fruits
- Spinach, kale, broccoli, zucchini
- Tomatoes, onions, peppers
- Bananas, apples, berries
🧂 Extras
- Protein powder (soy/pea; whey if lacto-vegetarian)
- Herbs, spices, salt, pepper
- Lemon juice, green tea
🧠 Nutrition Insights: Building Protein Without Meat
Plant proteins can be slightly less bioavailable, but variety and pairing across the day close the gap.
- Rice + beans
- Oats + yogurt
- Tofu + brown rice
- Lentils + whole-wheat roti
Hydration: Aim for ~2.5–3 L/day, especially with higher fiber intake.
🕐 When to Eat: Timing for Maximum Protein Synthesis
| Time | Example | ~Protein |
|---|---|---|
| 7:00 am | Breakfast smoothie | ~25 g |
| 10:00 am | Nuts or Greek yogurt | ~10 g |
| 1:00 pm | Lentil/tofu lunch | ~30 g |
| 4:00 pm | Protein snack | ~15 g |
| 7:00 pm | Quinoa + tofu dinner | ~25 g |
| 10:00 pm | Cottage cheese / soy milk | ~10 g |
💪 Vegetarian Diet for Muscle Gain
- Target a calorie surplus of ~+10–15%
- Include protein at every meal (distribute across 4–6 feedings)
- Lift progressively; sleep 7–8 h
Track output with the Calories Burned Calculator. Consider creatine, vitamin B12, and iron if needed.
⚖️ Vegetarian Diet for Weight Loss
Maintain a calorie deficit while keeping protein high. Use the BMR Calculator and Calories Calculator to set targets.
- Reduce added oils/sugars
- Prioritize high-fiber veggies & legumes
- Eat mindfully; hydrate; sleep well
Plant proteins increase satiety—supporting easier adherence.
🧩 Protein Quality: Complete vs Incomplete
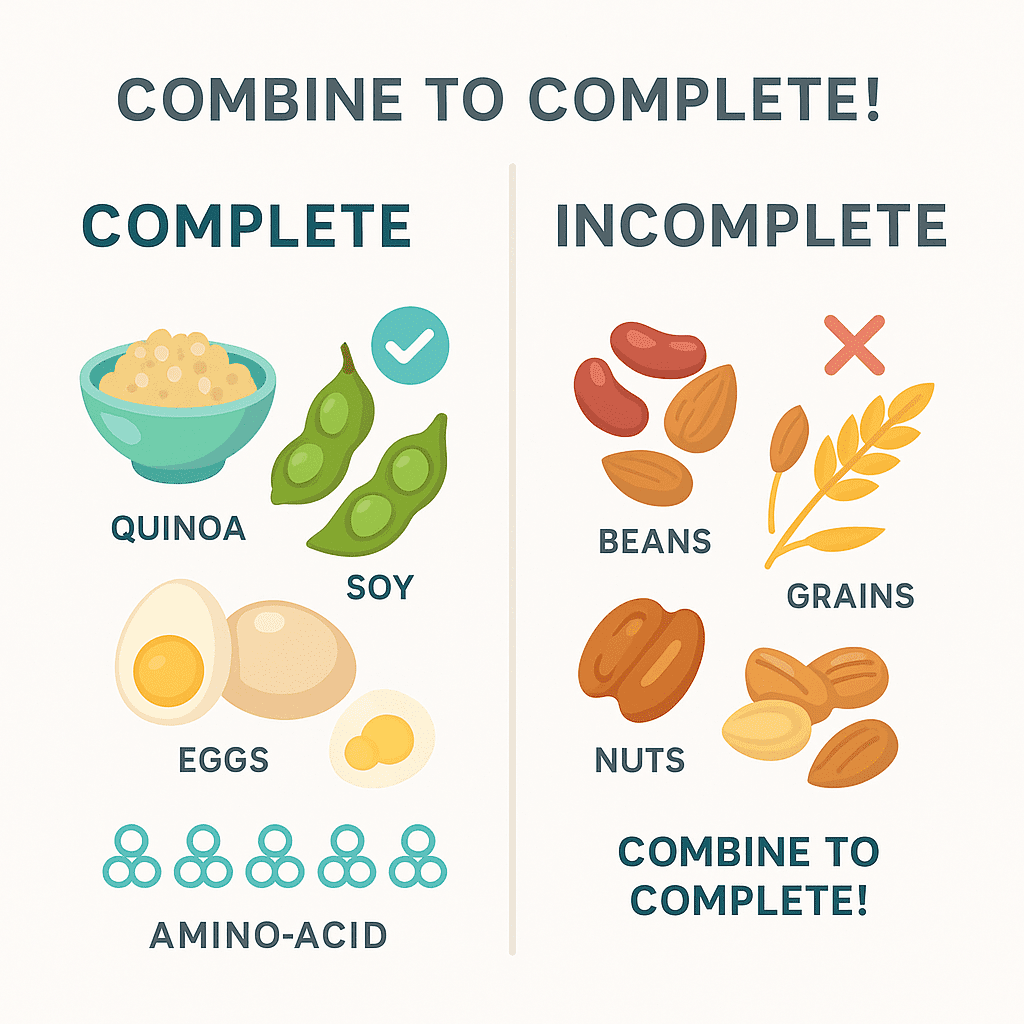
| Type | Examples | All Essential AAs? |
|---|---|---|
| Complete | Quinoa, soy, buckwheat, eggs | ✅ Yes |
| Incomplete | Beans, lentils, nuts, grains | ❌ No (pair them) |
🩺 Health Benefits of a Vegetarian Protein Plan
- Heart health (lower saturated fat)
- Better digestion (more fiber & antioxidants)
- Weight management (lower energy density)
- Lower inflammation (plant polyphenols)
- Longevity support (plant protein associations)
Replacing red meat with plant proteins is associated with reduced cardiovascular risk.
⚠️ Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Too few calories → fatigue & muscle loss
- Excess refined carbs crowding out protein
- Low B12/iron/zinc → add fortified foods or supplements
- Poor protein timing—spread across the day
- Low variety—rotate soy, legumes, grains, nuts, seeds
🧺 Sample Vegetarian Meal-Prep Schedule
| Day | Prep Task | Time | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sunday | Cook lentils, beans, quinoa | ~1 h | Refrigerate 4 days |
| Monday | Prepare smoothie packs | ~15 min | Freeze for week |
| Tuesday | Roast vegetables | ~30 min | Airtight containers |
| Thursday | Marinate tofu or paneer | ~20 min | Chill overnight |
| Friday | Bake chickpeas / make hummus | ~25 min | Keep 3–4 days |
🔍 Expert Insights: Is Vegetarian Protein Enough?
Registered dietitians and leading academic sources affirm: well-planned vegetarian diets can fully meet protein needs. You don’t need meat to be strong or lean—variety and smart pairing deliver complete amino acid coverage.
❓ FAQs
Can vegetarians get enough protein for bodybuilding?
Yes—120–150 g/day is achievable with lentils, tofu, tempeh, edamame, Greek yogurt, and strategic snacks.
Best plant proteins for muscle gain?
Soy (tofu, tempeh, edamame) is complete and well-studied; combine with legumes, grains, and dairy (if used).
Are protein powders necessary?
Convenient but optional—food first. Soy/pea blends are great choices.
Nutrient deficiencies to watch?
Vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3s; use fortified foods or supplements if needed.
How to make vegetarian meals more filling?
Combine protein + fiber + healthy fats (e.g., lentils + veggies + avocado or nuts).
🏁 Final Thoughts: Strong, Energized, and Meat-Free
You can thrive without meat. Use Protein Calculator, Ideal Weight Calculator, and Calories Burned Calculator to tailor intake to your goals—then fuel up with plants and be consistent.
About the Author
This article is written by the NutriFitCalc Team, a group of Food Science and Nutrition students who create simple, research-backed guides for healthy living.
We review global health sources like WHO and CDC to keep our content accurate and helpful.
