BMR Calculator
Learn what Basal Metabolic Rate is, how to calculate it with the Mifflin–St Jeor equation, and how to use it for smart calorie planning.
Why Understanding Your BMR Matters
Even at rest your body uses energy. Basal Metabolic Rate is the calories needed for vital processes such as breathing, blood circulation, cell repair, and temperature control.
The NutriFitCalc BMR Calculator estimates this quickly from your weight, height, age, and sex. Knowing BMR helps you manage weight, plan meals, and set realistic goals. It is the first step to understanding how your metabolism works.
What Is BMR
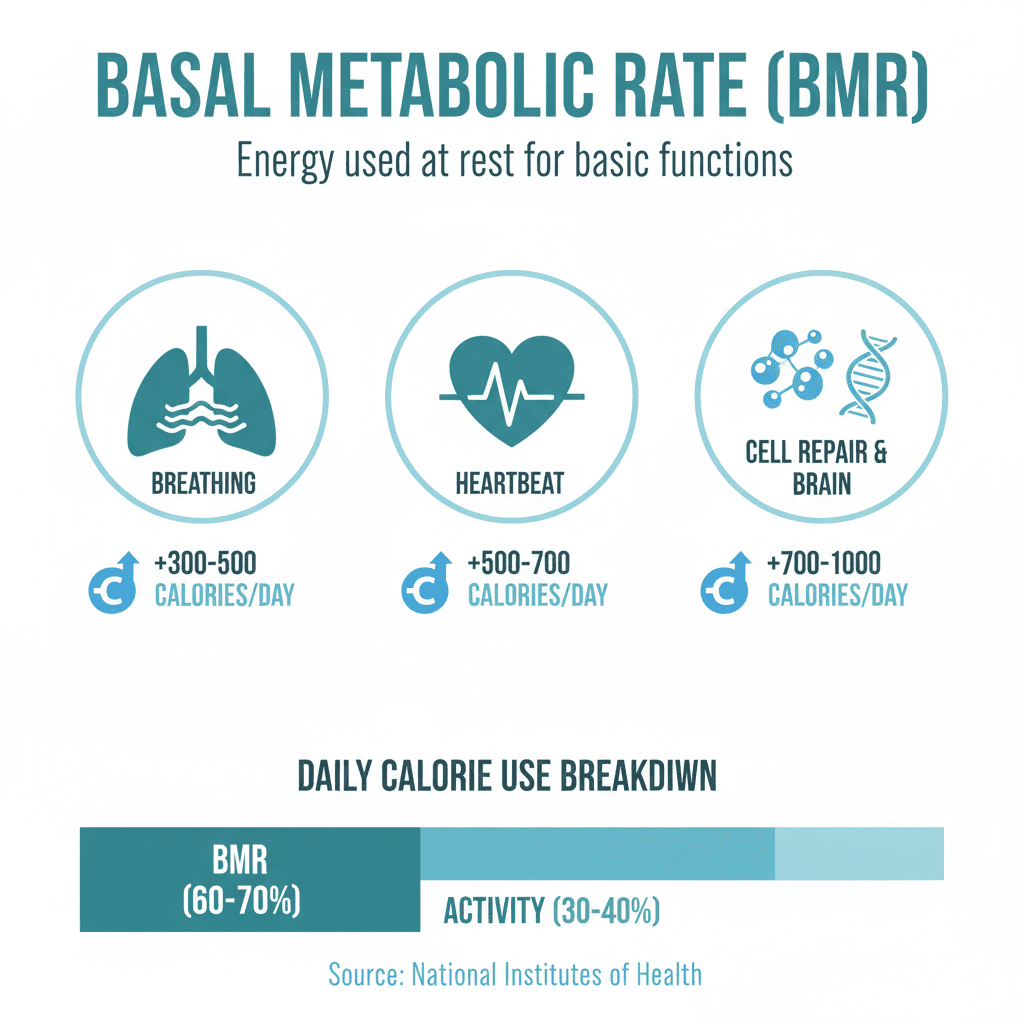
BMR is the energy your body uses at rest to maintain organ function. For many people it accounts for roughly 60 to 75 percent of total daily energy use.
- Oxygen and blood circulation
- Brain and nerve activity
- Cellular repair and growth
- Breathing and thermoregulation
Reference: Harvard Health Publishing
Calculate Your BMR
The NutriFitCalc BMR tool uses the Mifflin–St Jeor equation, widely used for accuracy.
Formulas
- Men: BMR = 10 × weight (kg) + 6.25 × height (cm) − 5 × age (years) + 5
- Women: BMR = 10 × weight (kg) + 6.25 × height (cm) − 5 × age (years) − 161
Example: Woman, 30 years, 60 kg, 165 cm → BMR ≈ 10×60 + 6.25×165 − 5×30 − 161 = 600 + 1031.25 − 150 − 161 ≈ 1,320 kcal/day.
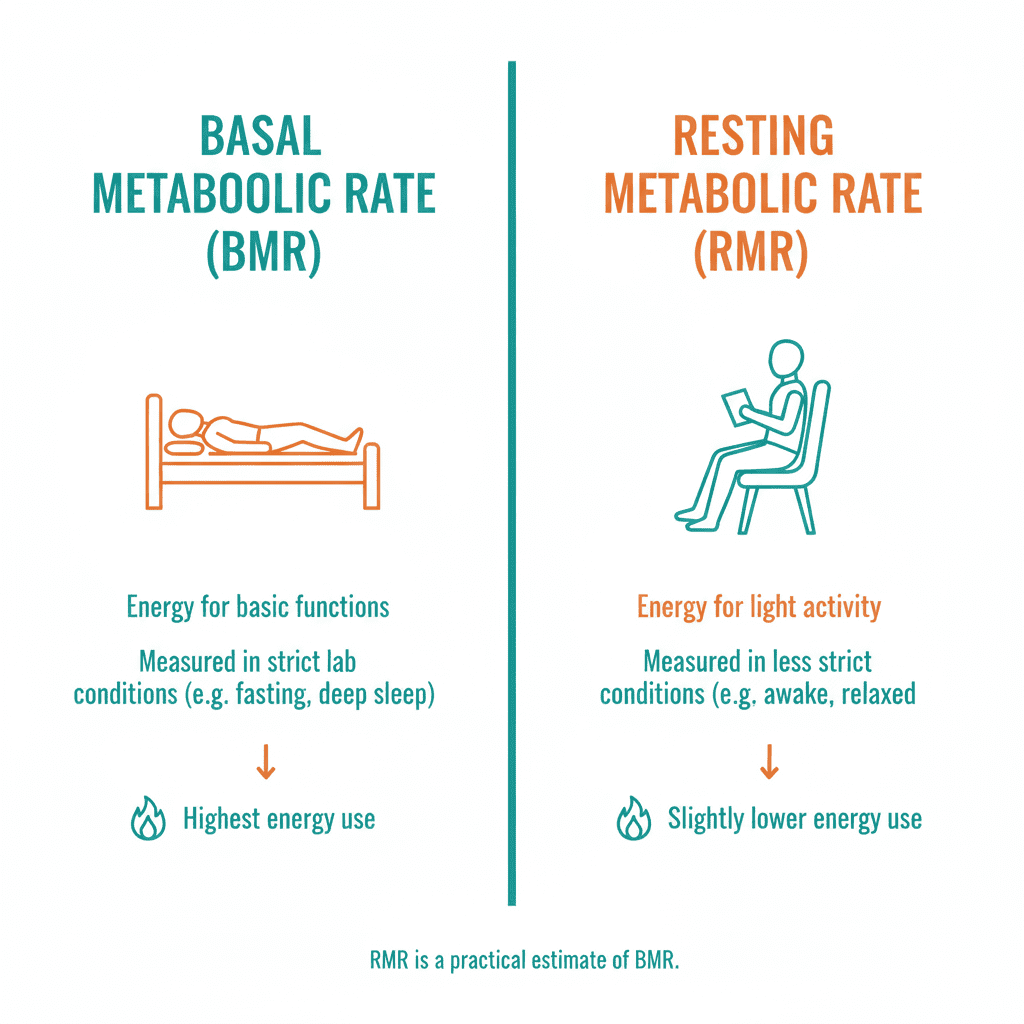
BMR vs RMR
Both measure resting energy use. RMR allows small movements such as sitting quietly and is often 5 to 10 percent higher than BMR. Understanding both can improve your estimate of total needs.
Reference: CDC Nutrition Basics
From BMR to Daily Calories
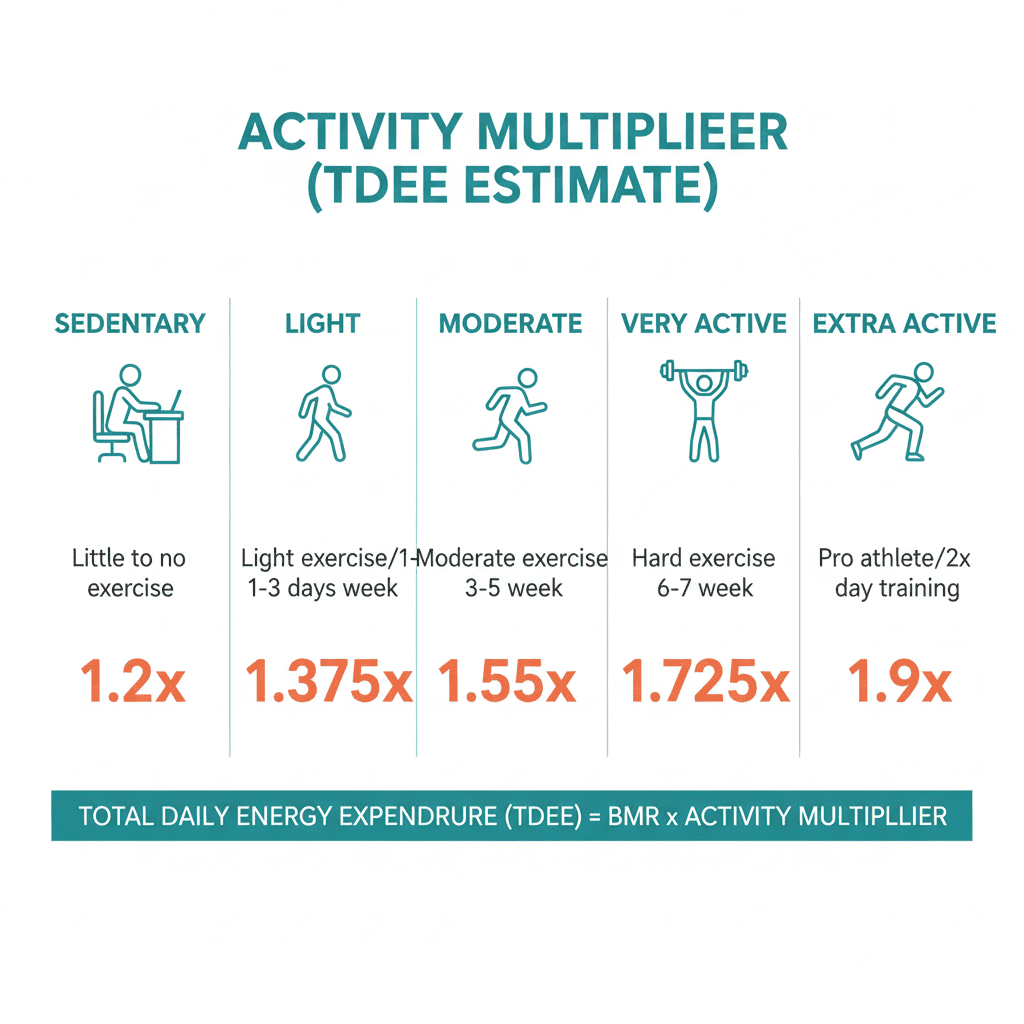
Multiply BMR by an activity factor to estimate Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE).
| Activity level | Multiplier | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | 1.2 | Little or no exercise |
| Lightly active | 1.375 | Light exercise 1–3 times per week |
| Moderately active | 1.55 | Moderate exercise 3–5 times per week |
| Very active | 1.725 | Intense exercise 6–7 times per week |
| Extra active | 1.9 | Hard physical job or daily intense training |
Using BMR for Weight Loss
A consistent modest deficit is effective. Many people target about 300 to 500 kcal below TDEE. Example: if TDEE is 2,000 kcal, eating about 1,600 to 1,700 may help reduce fat while preserving lean mass. Avoid extreme cuts that slow metabolism.
Using BMR for Muscle Gain
For lean gains, aim for a surplus of about 300 to 500 kcal above TDEE and pair with resistance training plus adequate protein.
Estimate and plan with:
How to Use the NutriFitCalc BMR Calculator
- Select your sex.
- Enter height and weight in centimeters and kilograms.
- Enter your age.
- Choose your activity level from sedentary to extra active.
- Tap Calculate BMR.
You will get your BMR, an estimated TDEE, and simple guidance for calorie planning.
Factors That Influence BMR
- Age: metabolism often slows with age.
- Sex: men usually burn more due to higher lean mass.
- Body composition: more muscle supports a higher BMR.
- Hormones: thyroid and insulin affect rate.
- Environment: cold exposure can raise BMR temporarily.
- Genetics: natural differences matter.
- Sleep and stress: poor sleep and high stress can lower calorie burn.
Reference: WHO Healthy Diet Guidelines
Practical Ways to Support Metabolism
- Lift weights to build and maintain muscle.
- Stay hydrated to support cellular processes.
- Include protein at each meal to raise the thermic effect of food.
- Eat a balanced breakfast if it helps you control appetite.
- Sleep 7 to 8 hours to balance appetite hormones.
- Manage stress to limit cortisol driven fat storage.
- Move often with short walks and stretch breaks.

BMR Myths
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| BMR is always high in thin people | Weight is not the only factor. Composition and hormones matter. |
| You cannot change metabolism | Training, protein intake, sleep, and stress control can improve it. |
| Eating less always speeds weight loss | Severe restriction can slow BMR and increase fatigue. |
| Men and women burn calories equally | Men often burn more due to higher lean mass. |
| BMR drops completely after 30 | Consistent training helps maintain a healthy rate at any age. |
BMR for Women vs Men
| Category | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Typical BMR range | ≈ 1,600–2,000 kcal | ≈ 1,200–1,600 kcal |
| Key factor | Muscle mass | Hormonal balance and composition |
| Primary goal | Maintain lean tissue | Strength support and steady energy |
Women can support BMR with strength training, balanced protein intake, and quality sleep.
Reference: National Institutes of Health
BMR and Calorie Deficit
BMR combined with activity gives TDEE. Eating below TDEE creates a deficit for fat loss. Many people aim for about 0.5 kg per week through a moderate deficit and consistent training. Avoid very large deficits that raise fatigue and nutrient risk.
FAQs
What is a normal BMR
It varies by age, sex, size, and lean mass. Use the BMR Calculator for a personal estimate.
How accurate is the NutriFitCalc BMR Calculator
It uses the Mifflin–St Jeor equation. Real world accuracy is often within about ten percent, and improves when you update inputs as your body changes.
Can I increase my BMR
Yes. Build muscle, stay hydrated, prioritize protein, sleep well, and manage stress.
What is the difference between BMR and TDEE
BMR covers basic functions at rest. TDEE equals BMR multiplied by activity to include daily movement and exercise.
Does age affect BMR
Yes. It often declines with age. Strength training and a protein forward diet can help slow the decline.
Conclusion
Your Basal Metabolic Rate is a foundation for a healthy lifestyle. The NutriFitCalc BMR Calculator clarifies how your body burns calories and how to align food choices with your goals. Start today, track your BMR, and adjust calories with purpose.